Causes of Bleeding in the Brain What You Should Know
Causes of Bleeding in the Brain What You Should Know
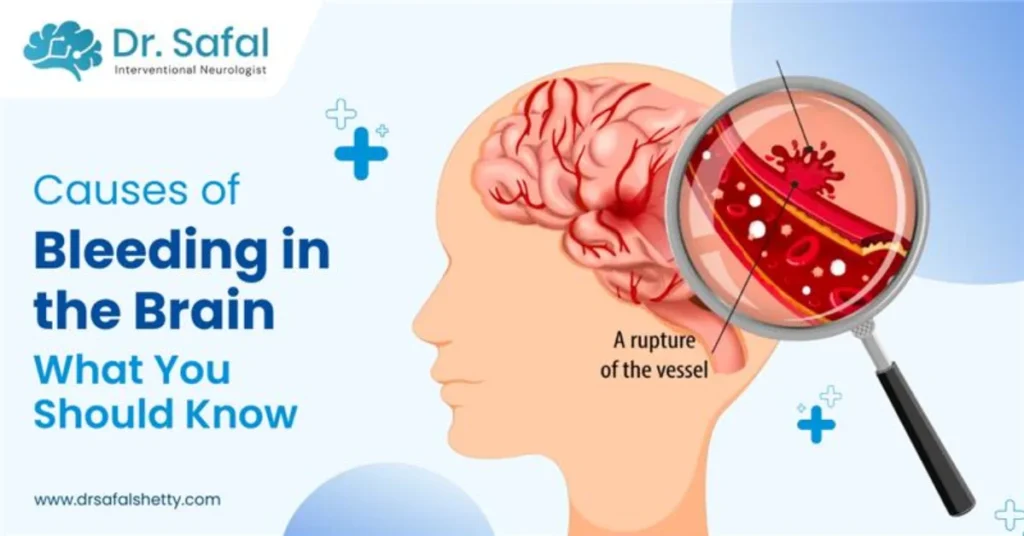
Bleeding in the brain. Sounds frightening, right? Indeed, it is one of the most serious medical emergencies that should never be taken lightly. In medical terms, it is called a brain haemorrhage or hemorrhagic stroke. It happens when a blood vessel in or around the brain ruptures and leaks blood into the surrounding tissue. This bleeding puts extra pressure on the brain, damages brain cells and disrupts the normal brain functioning.
But you might be wondering with a big question, why does this happen in the first place? What actually causes bleeding in the brain? Let’s break down the main culprits behind brain bleeds in a way that makes sense.
1. High blood pressure
Let’s start with the significant risk factor of brain bleeding. When the blood pressure stays elevated for so long, you are likely putting your blood vessels under constant stress. Overtime, this consistent high blood pressure weakens the walls of blood vessels and eventually might give way and burst.
The tricky part is, most people are not aware of their high blood pressure until something serious happens, because it doesn’t often alert you with any symptoms. This is the exact reason why every doctor recommends getting regular health checkups. When they say so, it’s not just nagging but a genuine vigilance.
2. Head injury or trauma
Probably, this is an intuitive cause for bleeding in the brain. A sudden blow to the head, due to an accident, a bad fall, or a sports injury, causes damage to the blood vessels in the brain and tear it to bleed.
Even a seemingly minor fall, which doesn’t cause any serious outside injury, can be dangerous, as bleeding may start slowly and symptoms might appear hours or even days later.
3. Weak or abnormal blood vessel
This is one of the relatively rare conditions that causes sudden and severe bleeding in the brain, often without prior symptoms. This is basically a weak spot in the blood vessel that can rupture to cause a type of bleeding in the brain.
In medical terms, this is categorised into two conditions.
- Aneurysm: A bulge in a blood vessel, like a small bubble
- Arteriovenous malformation (AVM): A tangled connection between arteries and veins that disrupts normal blood flow.
- AV fistula(Dural and Pial): A condition where there is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins.
Some people are born with these conditions due to abnormal blood vessel development, while others develop this rare condition over time due to factors like high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, trauma or venous thrombosis. Most of the time, people don’t even know they have one and are just living their lives with this little weak point in their brain. Scary, isn’t it?
4. Blood thinners and bleeding disorders
Blood thinners are lifesaving medications for many heart conditions. But they carry the increasing risk of bleeding in the brain. An iron twist, right?
Blood thinners are used to prevent blood clots, but they also make it hard for the blood to clot when it needs to.
Similarly, people with bleeding or clotting disorders are more vulnerable to spontaneous bleeding in the brain as their blood doesn’t clot properly. In such cases, even a small injury or rise in blood pressure can trigger bleeding.
5. Liver diseases and excess alcohol consumption
Your liver is like a behind-the-scenes hero when it comes to producing blood-clotting factors. Without them, even a small injury can lead to excessive bleeding. When the liver isn’t functioning well, it affects the blood’s ability to clot and leads to uncontrolled bleeding. People with severe liver disease might experience spontaneous bleeding without any obvious injury, because their blood is simply too thin to maintain the integrity of blood vessels.
Here is the catch. Chronic alcohol abuse is one of the leading causes of liver damage. Excessive alcohol consumption further worsens the problem by damaging blood vessels and increasing blood pressure. Over time, this combination raises the risk of brain bleeding significantly.
6. Brain tumors
Both cancerous and non-cancerous brain tumours can cause bleeding. Tumours often develop abnormally and disturb the blood vessels, which are fragile and more likely to rupture. In some cases, bleeding is what leads to the discovery of a brain tumour.
7. Infections Affecting the Brain
Certain infections can inflame blood vessels in the brain or weaken them. This inflammation increases the chance of rupture and bleeding. While this cause is relatively rare, it’s still an important one, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
FAQ
1. Can high blood pressure really cause bleeding in the brain?
Yes, absolutely. High blood pressure is one of the leading causes of brain bleeding. When blood pressure stays high for a long time, it weakens the walls of blood vessels in the brain. Over time, these weakened vessels can rupture, leading to bleeding.
2. Is bleeding in the brain always caused by injury?
No. While head injuries are a common cause, especially in accidents or falls, bleeding in the brain can also occur due to medical conditions like high blood pressure, blood-thinning medications, liver disease, or weak blood vessels. It doesn’t always involve trauma.
3. Can stress cause a brain bleed?
Stress alone doesn’t directly cause brain bleeds, but it can be a contributing factor. Chronic stress can lead to sustained high blood pressure, which is one of the main culprits behind brain haemorrhages.
4. Do brain bleeds cause permanent damage?
Not necessarily. The outcome depends on many factors, including the size of the bleed, its location, how quickly it was treated, and the person’s age and overall health.
5. What's the difference between a stroke and a brain bleed?
A brain bleed is actually one type of stroke, called a hemorrhagic stroke. However, most strokes (about 87%) are ischemic strokes, which happen when a blood vessel gets blocked and cuts off blood flow to part of the brain. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures and bleeds into the brain. Both are medical emergencies, but they require different treatments

Authored by Dr. Safal Sachidananda Shetty, an Interventional Neurologist & Stroke Expert in Bangalore with extensive clinical experience in stroke intervention, brain aneurysms, and complex neurovascular disorders. His mission is to educate, prevent, and provide advanced neurologic care using the latest medical innovations and minimally invasive procedures.
